
Earth Science and Engineering
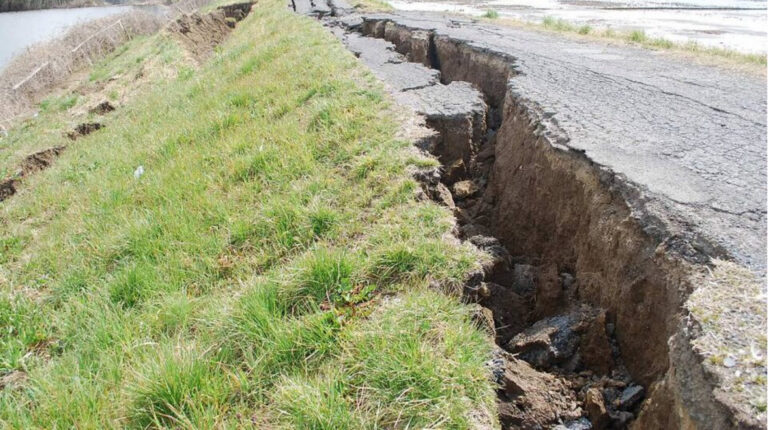
When Earth breaks the “rules”
A record-setting earthquake in Myanmar challenges how scientists predict future seismic hazards.
Page 1 of 1

Earth Science and Engineering
A record-setting earthquake in Myanmar challenges how scientists predict future seismic hazards.

Earth Science and Engineering
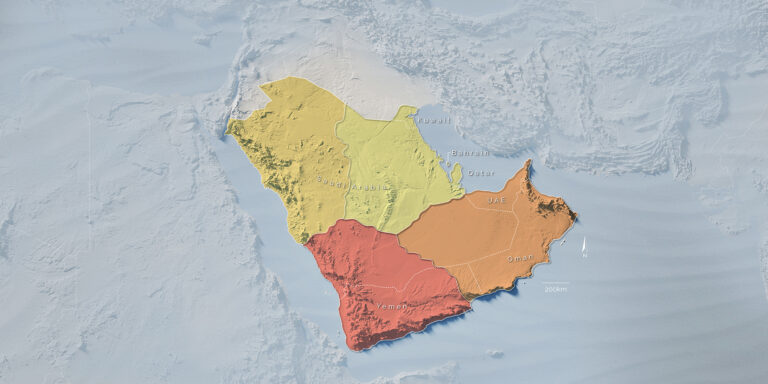
Beneath the deserts of Saudi Arabia lies a hidden record of Earth’s earliest continental history — a geological archive that could reshape our understanding of how Arabia was born.

Earth Science and Engineering
A precision remote sensing tool uses high-resolution ocean color data to predict both the scope and severity of coral bleaching.

Earth Science and Engineering
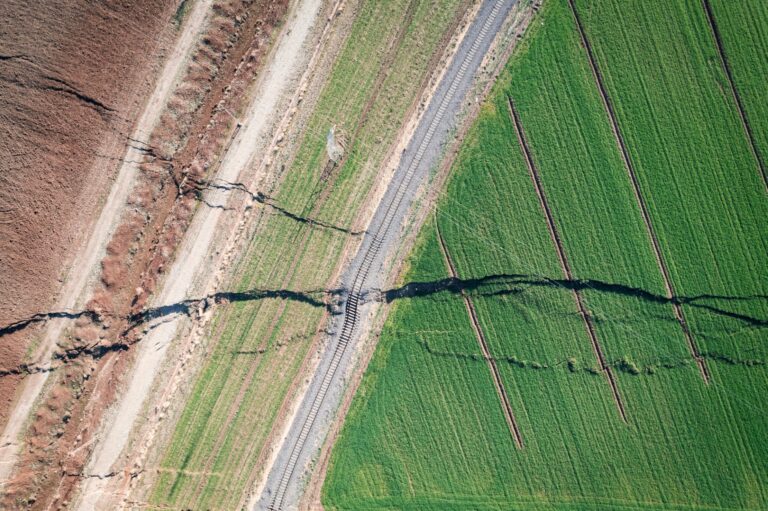
An image analysis technique shows that crustal damage from an earthquake can extend further than expected with implications for slip rate estimates and hazard assessment.
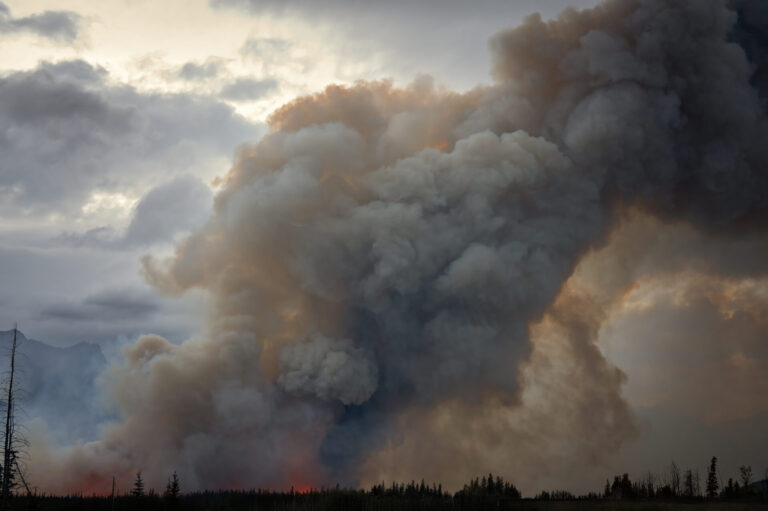

Chemical Engineering
Insight into how photoexcited biomass-burning organic aerosols boost sulfate formation could help control wildfire-driven air pollution.

Earth Science and Engineering
Climate research highlights future warming scenarios for the Arabian Peninsula.
Applied Mathematics and Computational Sciences
Higher temperatures have increased drought frequency and intensity over the last two decades, but the trend could be reversed in the next 20 years.
Earth Science and Engineering
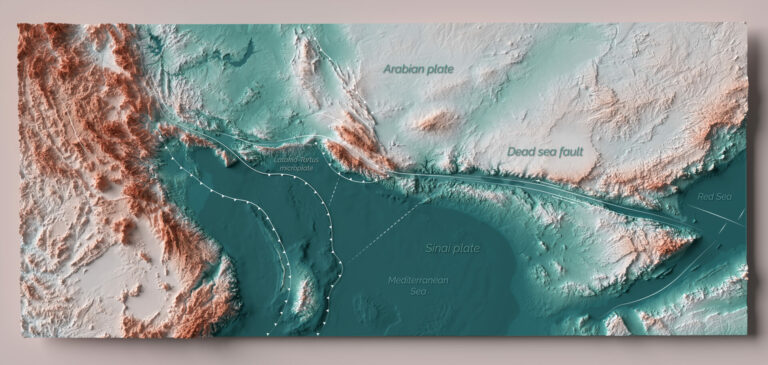
A new analytical technique enables reassessment of plate boundaries and improved slip rate estimations along the Dead Sea Fault.

Applied Mathematics and Computational Sciences
Long-term satellite data shows a significant cooling effect of vegetation on land surface temperature.

Applied Mathematics and Computational Sciences
A data-driven modeling system that reconstructs oceanic circulation of the Red Sea highlights the importance of developing region-specific historical datasets.

Earth Science and Engineering
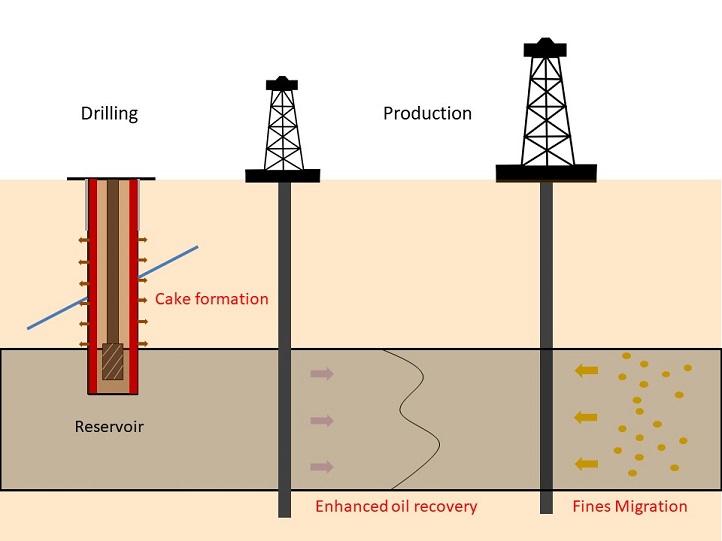
Computer simulations show how nitrogen injections can help flush oil from underground storage.

Earth Science and Engineering
Modeling air quality over the Arabian Peninsula reveals that pollution from anthropogenic sources is contributing to health risks and climate change.

Earth Science and Engineering
Seasonal phytoplankton blooms in the Al-Wajh lagoon differ from those in the adjacent Red Sea due to regional water dynamics and nutrient availability.
Earth Science and Engineering
A comprehensive study suggests the Arabian plate is geologically stable and capable of withstanding long-term forces from surrounding tectonic activity.

Earth Science and Engineering
Simulations show that solar panel installations could go a long way toward addressing Saudi Arabia’s growing water crisis.

Earth Science and Engineering
Modeling the impact of meteorological forces on the Red Sea shows that winds in the southern part of the sea modulate sea-level surges across the basin.

Earth Science and Engineering
Warmer waters in the central tropical Pacific in recent decades have led to shifts in atmospheric wind jets, bringing more winter rainfall to the eastern Arabian Peninsula and less to the south.

Earth Science and Engineering
Saudi Arabia might not be shaken from its ambitious development goals, but it cannot rule out large earthquakes entirely.
Earth Science and Engineering
Studying slow, gentle and previously undetectable events will help reveal the origins of damaging earthquakes.

Earth Science and Engineering
An extended epidemic model that accounts for uncertainty and the latest data can better predict the evolution of pandemics.

Earth Science and Engineering
Trends in heat discomfort are more subtle than expected across Saudi Arabia and beyond.

Earth Science and Engineering
Geologic structures and deposits below planetary surfaces can be mapped faster than ever.

Earth Science and Engineering
Ozone depletion following the Toba eruption around 74,000 years ago compounded the ensuing volcanic winter and caused a human population bottleneck.

Earth Science and Engineering
A detailed analysis combining seafloor mapping and earthquake and gravity data shows that the oceanic crust under the Red Sea is older than previously thought.

Earth Science and Engineering
The timing of phytoplankton blooms in the Red Sea could help determine next year’s fish catch.

Earth Science and Engineering
A new analysis of satellite data gives a detailed view of how extreme dust events have changed over time.

Earth Science and Engineering
Red Sea atlas of algal blooms reveals the need for more sustainable fish farming.

Earth Science and Engineering
A model for the southeastern California lithosphere suggests that a strong upper crust overlies weaker lower rock layers.

Earth Science and Engineering
Modeling shows that volcanic eruptions can cause changes in global climate, if the timing is right.

Earth Science and Engineering
An all-inclusive climate model for the entire Red Sea region is supporting Saudi Arabia’s plans for a sustainable future.

Earth Science and Engineering
Analysis of abnormally deep earthquakes may lead to improved seismic forecasting.

Earth Science and Engineering
A high-resolution atmospheric assessment for the northern Red Sea coast in Saudi Arabia shows the region has some of the best air quality in the Kingdom.

Earth Science and Engineering
Modeling shows that coral reefs off the east coast of Saudi Arabia play a vital role in protecting the coastal zone.
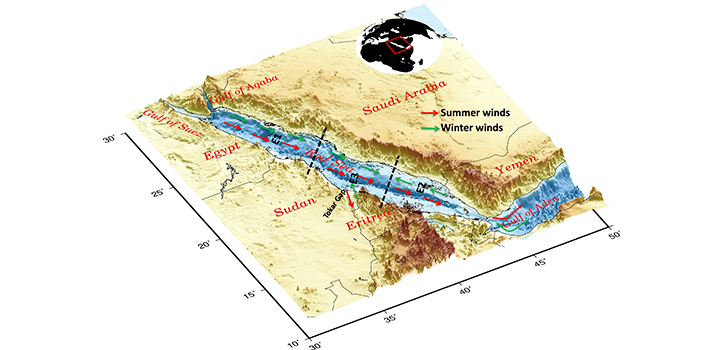
Earth Science and Engineering
Extra caution is required in developing climate forecasts of enclosed seas.
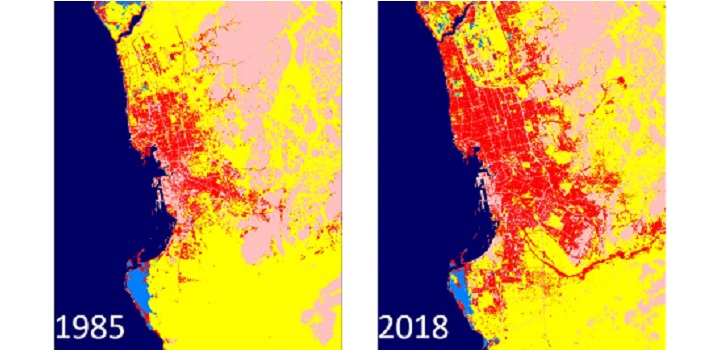
Earth Science and Engineering
Understanding how storms unleash more rain over cities in the desert could improve water security in Saudi Arabia.

Earth Science and Engineering
Simulations reveal unexpected connections in the Red Sea basin that could help marine conservation.
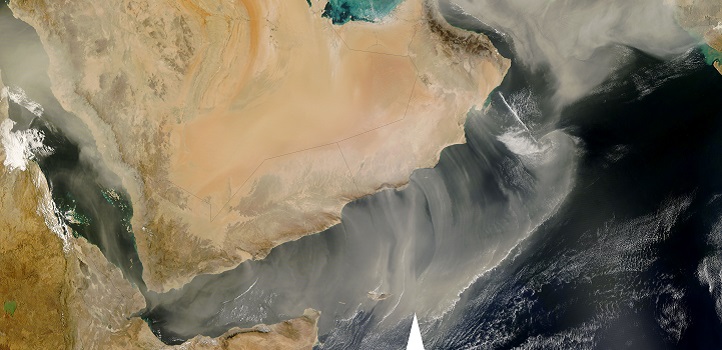
Earth Science and Engineering
Summer dust has been increasing over the Arabian Peninsula for the past decade with global implications.
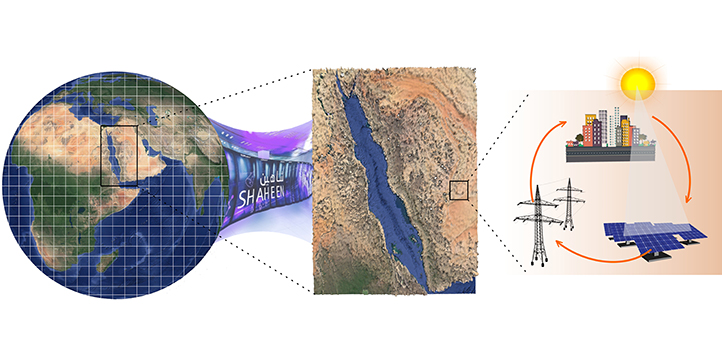
Earth Science and Engineering
Mapping variations in sunlight across the Arabian Peninsula reveals a bright future for solar energy in the region.
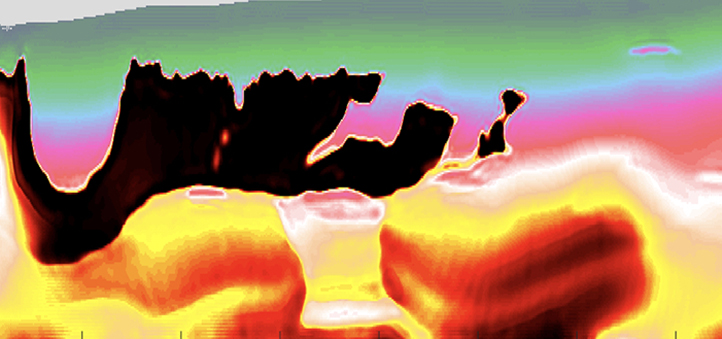
Earth Science and Engineering
Automated imaging of underground salt bodies from seismic data could help streamline oil and gas exploration.

Earth Science and Engineering
Exploring the links between natural climate cycles and the sea-surface temperature of the Red Sea reveals a cooling trend during the next few decades.
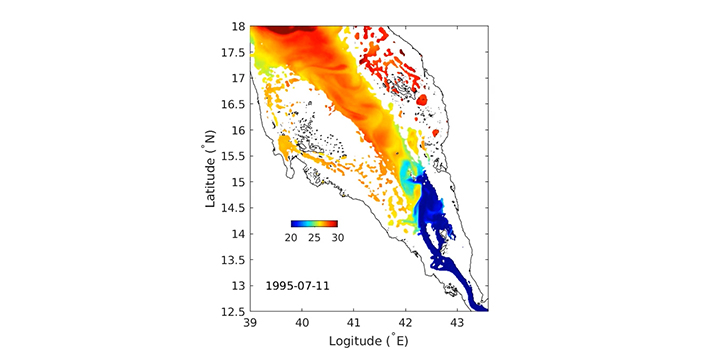
Earth Science and Engineering
Powerful computer simulations are revealing new insights into water exchanges between the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden.

Earth Science and Engineering
A remote sensing algorithm offers better predictions of Red Sea coral bleaching and can be fine tuned for use in other tropical marine ecosystems.
Earth Science and Engineering
Algal blooms in the Red Sea can be detected with a new method that accounts for dust storms and aerosols.

Earth Science and Engineering
World-class computing facilities at KAUST enable researchers to tackle complex questions in climate science and oceanography.
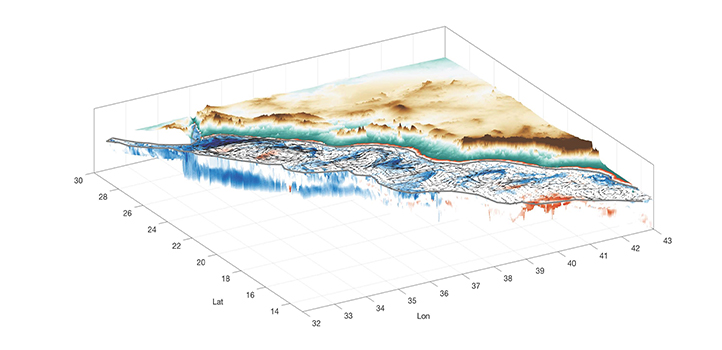
Earth Science and Engineering
Modeling the 3D structure of Red Sea eddies shows how transport of energy and biochemical materials influences circulation patterns in the Red Sea.
Earth Science and Engineering
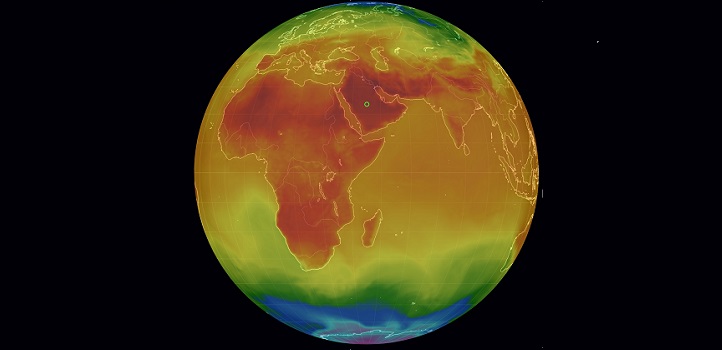
Investigating links between surface air temperatures and large-scale circulation patterns builds understanding of climate variability in the Arabian Peninsula.

Earth Science and Engineering
Modeling shows that the Indian summer monsoon can trigger heatwaves and sandstorms on the Arabian Peninsula.
Earth Science and Engineering
A comprehensive model for simulating mudcake growth during oil extraction could transform well-drilling protocols.

Earth Science and Engineering
Volcanic eruptions in Mexico and the Philippines can lead to atmospheric changes that favor the ventilation of deep water in the Red Sea.

Earth Science and Engineering
Advanced analysis of seismic data could lead the next wave in oil exploration.
Earth Science and Engineering
Color changes in the northern Red Sea indicate rising sea temperatures could significantly impact tropical marine ecosystems.

Earth Science and Engineering
Geophysical modeling of one of the world’s most important fossil sites reveals the history of the site where early humankind evolved.
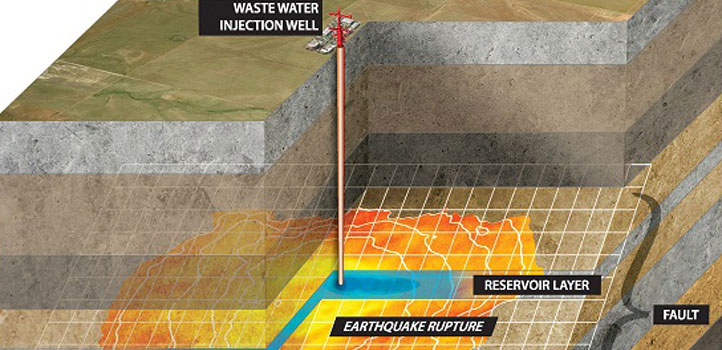
Earth Science and Engineering
A model incorporating the physics of ruptures provides valuable information about human-induced earthquakes.

Earth Science and Engineering
Study design allows more rigorous evaluation of complex healthcare interventions.

Earth Science and Engineering
Physicists are playing unexpected roles in meeting future global energy challenges by modeling technologies such as fracking.
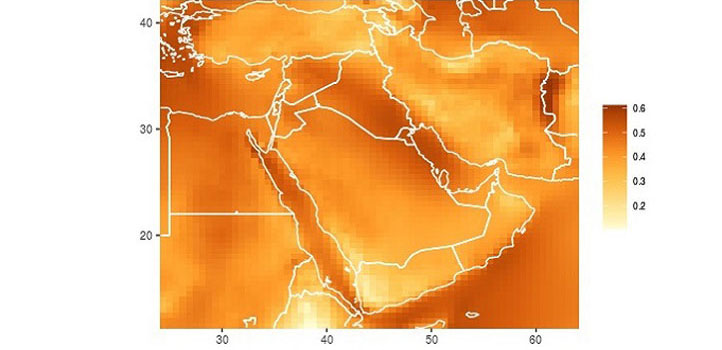
Earth Science and Engineering
Wind turbines suspended high in the sky have potential as an alternative power source for Saudi Arabia.
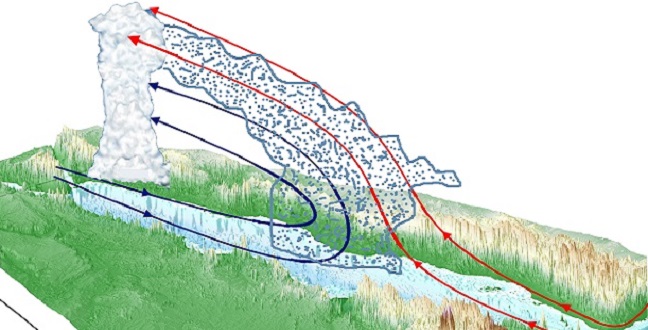
Earth Science and Engineering
Modeling leads to a better understanding of the role El Niño plays in increasing rainfall along the coast of the Red Sea.

Earth Science and Engineering
Wind intensities and wave heights in the Red Sea are decreasing over time—potential for a significant impact on its ecosystem.

Earth Science and Engineering
Atlantic surface circulation transports high loads of plastic debris to remote Arctic waters.

Earth Science and Engineering
Studying dusty air, especially in the Middle East, which is part of the Earth’s notorious dust belt, has both local and global significance.
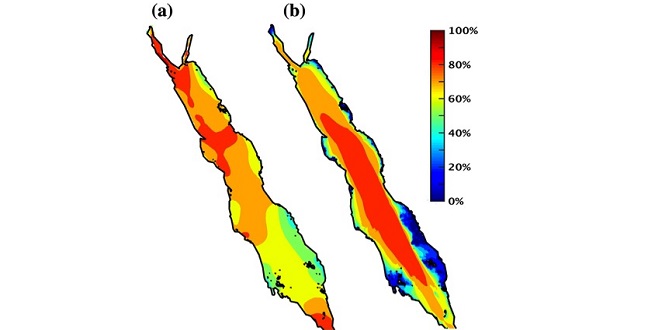
Earth Science and Engineering
Advanced numerical models are helping researchers identify potential sites to exploit offshore wind and wave energy in the Red Sea region.
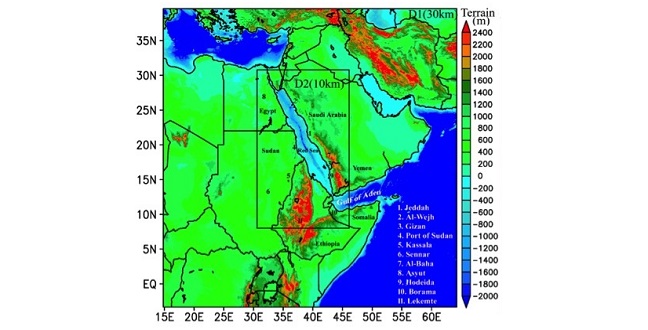
Earth Science and Engineering
An advanced numerical model is helping researchers better understand the variability of the Red Sea’s climate patterns.

Earth Science and Engineering
Satellite radar image analysis reveals that rifting in Iceland exhibits simultaneous horizontal and sideways movement.

Earth Science and Engineering
High-resolution modeling improves understanding of dust flow from Africa across the Red Sea toward the Arabian peninsula.

Earth Science and Engineering
Surface deformation caused by magma rising within the crust may in turn have prevented a volcanic eruption in Saudi Arabia.
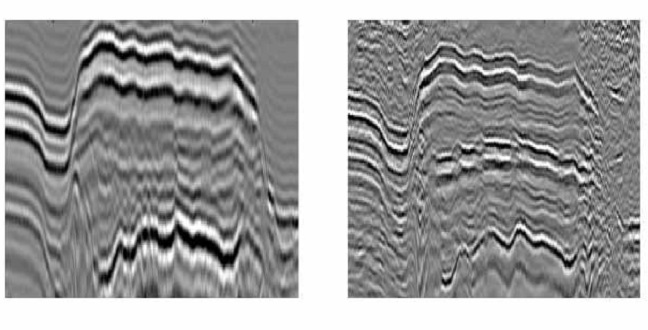
Earth Science and Engineering
A signal processing technique that makes use of seismic echoes is able to image subsurface geology at unprecedented resolution.
Earth Science and Engineering
Current models that predict ocean surface conditions overestimate wave patterns in the middle of the Red Sea.
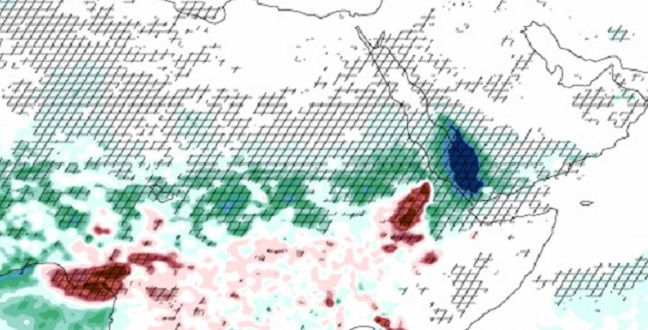
Earth Science and Engineering
Dust plays a critical role in determining rainfall over the Middle East and North Africa.

Earth Science and Engineering
Ship-based studies of dust levels above the Red Sea reveal significant variations and confirm the reliability of satellite monitoring.

Earth Science and Engineering
Modelling reveals how atmospheric dust influences daytime patterns of energy transfer from sunlight.
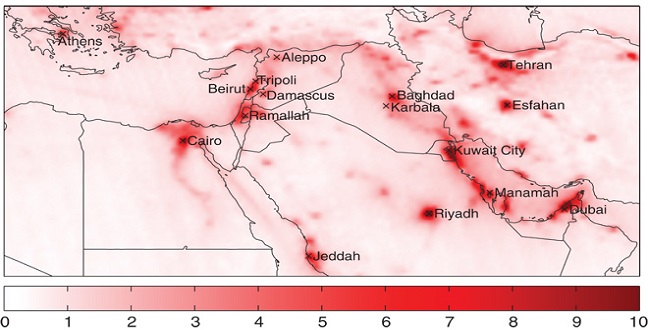
Earth Science and Engineering
Conflict and economic crises, combined with pollution control measures, are changing the air above the Middle East.

Earth Science and Engineering
The emergence of two volcanic islands in the Red Sea suggests a larger underlying event linked to African-Arabian plate separation.
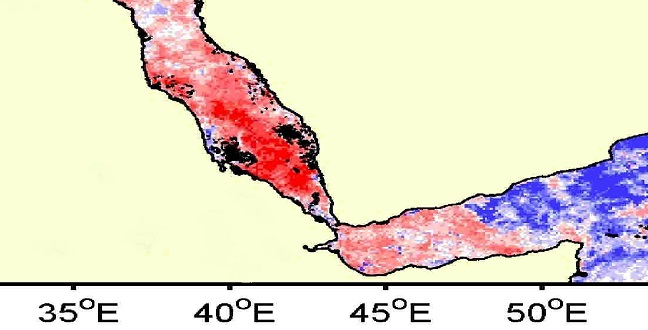
Earth Science and Engineering
A warmer Red Sea may be more productive due to the influence of winter monsoons.

Earth Science and Engineering
An underwater landslide triggered by the 2011 earthquake in Japan may have exacerbated the resulting tsunami.

Earth Science and Engineering
KAUST’s Earth Science and Engineering Program is underpinned by a drive to develop sustainable ways to get the best from natural resources and quantify environmental hazards.

Earth Science and Engineering
First-time reports of the statistical properties of ‘whirlpools’ show they are frequent and seasonal.