Earth Science and Engineering
The Arabian plate is holding steady
A comprehensive study suggests the Arabian plate is geologically stable and capable of withstanding long-term forces from surrounding tectonic activity.
To better understand the earthquake hazards facing the Arabian Peninsula, KAUST researchers have completed a comprehensive analysis of motion measurements for the entire Arabian tectonic plate.
The results provide new information on how the Arabian plate is moving with respect to its neighboring tectonic plates, which is critical for estimating the size and frequency of damaging earthquakes at plate boundaries. Importantly, the study also shows that the Arabian plate is internally remarkably stable and will continue to withstand pressures from continental collision in the northeast and the breakup of plates in the south for the foreseeable future.
Geodetic GPS measurements from 168 stations located across the Arabian plate were combined and processed by Renier Viltres, Sigurjón Jónsson and colleagues at KAUST, together with an international team. The data were collected continuously for up to 17 years, providing a far larger and more complete dataset than in previous studies.
“By combining these GPS measurements, we’ve quantified motions at different spatial scales for the entire Arabian plate,” says Viltres. “Normally, just a handful of GPS stations are enough to estimate the rate and direction of relative motions at the plate boundaries, but this new level of detail goes far beyond that.”
The researchers combined the GPS measurements with kinematic block modeling — a simplified description of tectonic plates as rotating rigid blocks that interact with each other at narrow boundaries. The model assesses the type and level of earthquake activity at the different boundaries between the blocks. The team then examined how the movements correspond to tectonic-related activity at plate boundaries and provided improved large-scale motion quantification of the whole Arabian plate.
“We were surprised at the remarkable stability of the Arabian plate, despite the push and pull forces associated with continental collision in the northeast and plate breakup in the south,” says Viltres. “The plate moves as a single block, and the motion of the plate relative to its major neighboring plates has likely remained unchanged for the last 13 million years.”
On a smaller scale, however, the researchers found localized deformation that likely stems from human activity — namely, the widespread extraction of water from underground aquifers. This supports previous studies that used satellite images to examine the impact of groundwater pumping.
“Our results come at a critical moment when the Kingdom’s economic and urban development plans include areas exposed to significant seismic and volcanic hazards,” says Jónsson. “We hope our study will help earthquake hazard assessments in these areas and lead to better planning and appropriate standards for construction.”
References
- Viltres, R., Jónsson, S., Alothman, A.O., Liu, S., Leroy, S., Masson, F., Doubre, C. & Reilinger, R. Present-day motion of the Arabian plate. Tectonics 41, e2021TC007013 (2022).| article
You might also like

Earth Science and Engineering
When Earth breaks the “rules”

Earth Science and Engineering
Unearthing Arabia’s ancient foundations: New insights from the Ha’il terrane

Earth Science and Engineering
Sensing color cues to monitor coral health in the Red Sea
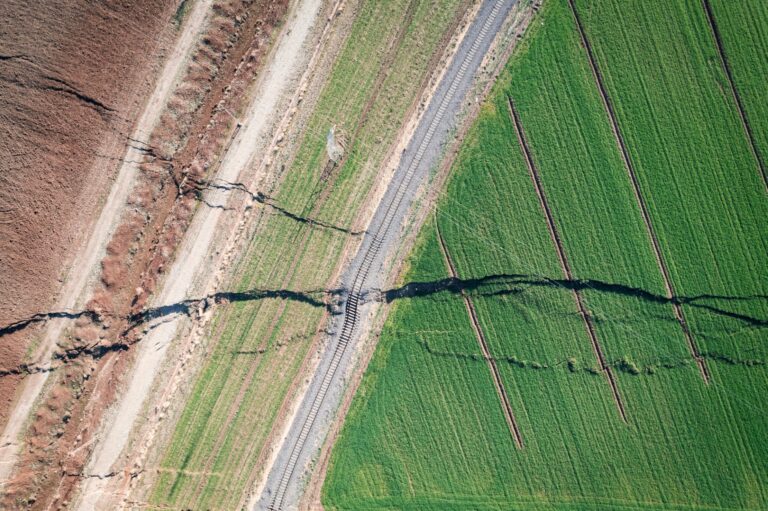

Earth Science and Engineering
Kahramanmaraş earthquake study showcases potential slip rate errors

Chemical Engineering
Unveiling the role of biomass-burning aerosols in atmospheric reactions

Earth Science and Engineering
Feeling the heat across the Middle East
Applied Mathematics and Computational Sciences
Past and future drought patterns across the Arabian Peninsula
Earth Science and Engineering




