Mechanical Engineering
Slippery superfluids push jets to breaking point
Improved imaging of liquid jet sprays can impact fields ranging from inkjet printing to oil and gas processing.

KAUST researchers are studying superfluids to better understand and predict the behavior of jet breakups. © 2020 KAUST
KAUST researchers are studying superfluids to better understand and predict the behavior of jet breakups. © 2020 KAUST
A unique type of helium that can flow without being affected by friction has helped a KAUST team better understand the transformation of rapidly moving liquids into tiny droplets.
Everyday occurrences, such as taking a shower or turning on the kitchen faucet, involve an intriguing physical phenomenon known as jet breakup. When a liquid exits a nozzle and encounters something it cannot immediately mix into—a gas, for example—it forms a cylinder. Quickly, small surface perturbations and various forces cause the liquid tube to break apart into droplets. The entire cylinder either pinches off into droplets one at a time at the tip, takes on a wavy or corkscrew-like structure, or atomizes into a fine spray.
Since the late 1800s, researchers have tried to understand and predict the behavior of jet breakups using classical theories of viscosity, aerodynamics and surface tension. However, many earlier studies present conflicting evidence about where to draw the line between different breakup modes—a problem that could impact manufacturers looking to optimize spray technologies.
“Engineers are interested in knowing the size and direction of the droplets formed and how far from the nozzle the jet stays intact,” notes Nathan Speirs, a researcher in Sigurdur Thoroddsen’s lab at KAUST. “There’s so much variety in the ways liquid jets break up.”
To update this field for the 21st century, the Thoroddsen group collaborated with researchers at the University of California, Irvine, to build a device capable of reaching temperatures near absolute zero with windows for viewing with high-speed cameras. At these chilly depths, liquid helium can take on a range of different behaviors, including as a frictionless superfluid.
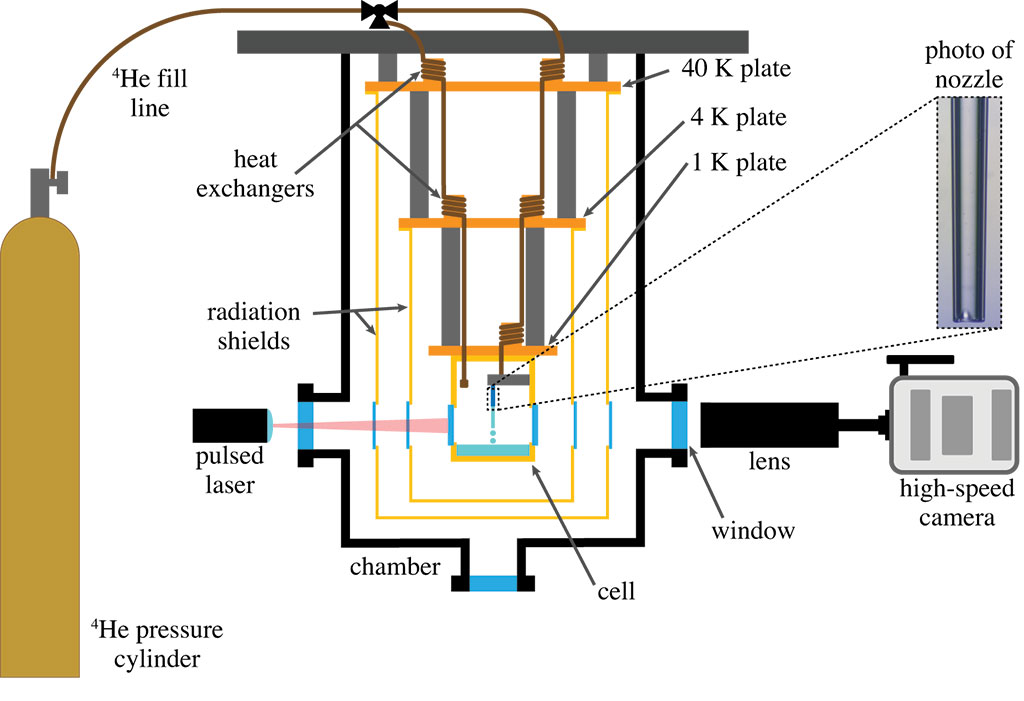
The experimental setup used by the team to capture the transformation of rapidly moving liquids into tiny droplets.
© 2020 KAUST
The experimental setup is tricky to work with because “when liquid helium becomes superfluid, the absence of viscosity allows it to escape from the tiniest of imperfections, which we call superleaks,” says Kenneth Langley, another member of Thoroddsen’s team. “We have to be very careful when closing the cell, and once it’s shut, there’s no way to adjust what’s inside.”
The detailed images produced using the new low-temperature device enabled the KAUST team to precisely quantify jet breakup regimes and identify physical factors overlooked by previous studies.
“Our results show that the gas and liquid flows are equally important in the interface region, an idea neglected by most other studies,” says Speirs. “The irregular shapes of the droplets formed are quite interesting as well, and we hope to analyze them in more detail,” adds Langley.
References
- Speirs, N.B., Langley, K.R., Taborek, P. & Thoroddsen, S.T. Jet breakup in superfluid and normal liquid 4He. Physical Review Fluids 5, 044001 (2020).| article
You might also like

Mechanical Engineering
Cracking clean fuel combustion

Mechanical Engineering
Tiny sensor could transform head injury detection
Mechanical Engineering
Electrocatalytic CO2 upcycling excels under pressure

Chemical Engineering
Rethinking machine learning for frontier science

Mechanical Engineering
Falling water forms beautiful fluted films

Mechanical Engineering
Innovative strain sensor design enables extreme sensitivity
Mechanical Engineering
Turbulent flow shows surprise patterns that could help boost efficiency

Mechanical Engineering




