Mechanical Engineering
Bouncing bubbles shake up emulsion studies
Collisions of tiny air bubbles with water surfaces can reveal fundamental characteristics of foamy mixtures.
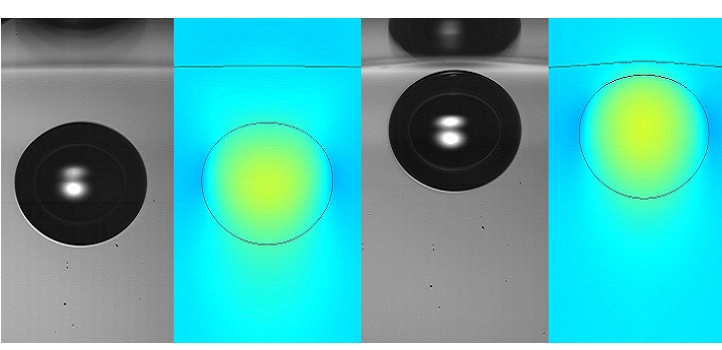
KAUST researchers are using the fastest video cameras ever to clarify how molecular-scale changes to water surfaces may impact the performance of industrial-scale purifications. © 2020 KAUST; Ivan Vakarelski
KAUST researchers are using the fastest video cameras ever to clarify how molecular-scale changes to water surfaces may impact the performance of industrial-scale purifications. © 2020 KAUST; Ivan Vakarelski
Some of the fastest video cameras ever developed have been used by KAUST researchers to clarify how molecular-scale changes to water surfaces may impact the performance of industrial-scale purifications.
One factor that influences the stability of emulsions is how quickly small bubbles or droplets join together into larger droplets. Ivan Vakarelski, a research scientist in Sigurdur Thoroddsen’s lab, notes that this type of coalescence is driven by variables ranging from bubble size, collision speed, and the “freedom” of molecules located at liquid surfaces.
“When liquids contact a solid, they tend to stick due to strong molecular forces. In contrast, a clean liquid exposed to air can move along relatively easily—we call that a mobile interface,” explains Vakarelski. “It’s a fundamental property that determines the behavior of many foams and emulsions.”
Recently, Thoroddsen and his team used their expertise at high-speed imaging to observe collisions between air bubbles formed in a perfluorocarbon, a liquid with similar viscosity to water that can be refined to an ultrapure state. To their surprise, these bubbles did not coalesce as fast as anticipated. Instead, the high mobility of the air- perfluorocarbon interface caused the bubbles to repeatedly bounce off each other before merging.
In their latest work, the KAUST researchers broadened their investigations to the world’s most important liquid—water. A clean air-water interface is supposed to be mobile, however, numerous studies suggest they have low molecular freedom because they are highly susceptible to contamination.
To resolve this quandary, Vakarelski helped design an experiment that used thin films of fatty acids to completely immobilize a free water surface. Then, they released millimeter-sized air bubbles that floated to the interface and crashed into it. When images of the rebounding bubbles were compared to ones taken on purified water surfaces, the team saw that the fatty acid film drastically reduced the degree of bouncing.
“A common belief is that once water is exposed to the atmosphere in a laboratory, it’s impossible to keep it clean enough to be mobile,” says Vakarelski. “However, our study shows that this is not correct—a standard purification device produces an interface that bounces bubbles back quite strongly.”
Successful tests of this approach with other liquids, such as ethanol, indicate that bubble analysis could help solve problems in food processing applications as well as chemical production.
References
- Vakarelski, I., Yang, F. & Thoroddsen, S.T. Free-rising bubbles bounce stronger from mobile than immobile water-air interfaces. Langmuir. 36, 5908-5918 (2020).| article
You might also like

Mechanical Engineering
Cracking clean fuel combustion

Mechanical Engineering
Tiny sensor could transform head injury detection
Mechanical Engineering
Electrocatalytic CO2 upcycling excels under pressure

Chemical Engineering
Rethinking machine learning for frontier science

Mechanical Engineering
Falling water forms beautiful fluted films

Mechanical Engineering
Innovative strain sensor design enables extreme sensitivity
Mechanical Engineering
Turbulent flow shows surprise patterns that could help boost efficiency

Mechanical Engineering




