Bioscience
Parasite scan yields new targets
Enzymes crucial to parasite growth offer clues in fight against malaria.
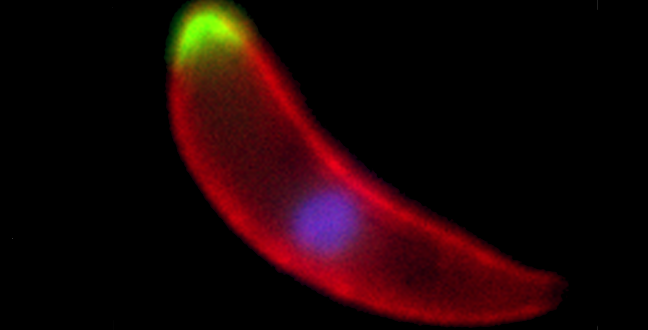
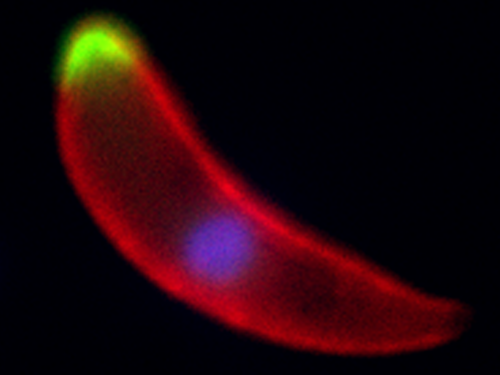
A Plasmodium ookinete, the developmental stage that invades the mosquito midgut, with two different phosphatases shown in green, the surface of the parasite marked in red and the nucleus stained in blue
© Guttery, D.S. et al./Cell Host & Microbe
Nearly half the world’s population is at risk from malaria, a disease that kills more than 600,000 people globally each year. Research into an ‘on/off switch’ within the genes of the parasite that causes malaria has revealed enzymes that control how cells develop and differentiate. Identifying these enzymes could pinpoint targets for future treatments of the deadly disease.
Malaria is caused by infection from mosquito borne parasitic protozoans of the Plasmodium type. This single-celled microorganism progresses through several distinct life cycle stages, with each stage affected by a suite of enzymes that modify phosphate tags on other proteins to switch them ‘on’ or ‘off’.
During the development stages of Plasmodium, a lot of research has scrutinized the role of enzymes that chemically add the phosphate groups. However there has been little research into the role of enzymes that remove the phosphate tags, known as protein phosphatases.
Using a range of molecular and biochemical techniques, Rita Tewari and colleagues at the University of Nottingham, in collaboration with researchers from KAUST, Oxford and London, studied the genes coding each phosphatase enzyme in Plasmodium berghei, the mouse-infective relative of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum1.
The research team focused on how the phosphatases affect the parasite’s life cycle in infected mice.
“Our comprehensive analysis revealed the unique and essential roles of individual protein phosphatases in malaria parasite development,” says Stefan Arold, associate professor in the Biological and Environmental Science and Engineering Division at KAUST.
The study revealed around 30 such genes in each species. Importantly, most of the mouse parasite’s phosphatases were nearly equivalent to the human parasite’s versions of these same enzymes.
What’s more, the team discovered that 16 of the 30 genes encoding protein phosphatases in P. berghei were essential for parasite growth in the mouse. An additional six phosphatase genes were needed for the parasite to complete its life cycle in the mosquito.
To characterize the operation of the genes that encode protein phosphatases, the team analyzed several physical and functional features. These included the expression pattern of phosphatase genes, the gene interaction profile, and the three-dimensional structural features of the phosphatase enzymes in P. berghei parasites.
The team observed distinct expression patterns for each phosphatase at various life stages of the parasite, including key roles in its sexual and asexual development.
“Our results strongly encourage targeting protein phosphatases to combat malaria, and provide a specific list of protein phosphatases as prime targets,” says Arnab Pain, one of the lead authors and associate professor of bioscience at KAUST.
References
- Guttery, D.S., Poulin, B., Ramaprasad, A., Wall, R.J., Ferguson, D.J. et al. Genome-wide functional analysis of Plasmodium protein phosphatases reveals key regulators of parasite development and differentiation. Cell Host & Microbe 16, 128–140 (2014). | article
You might also like

Bioscience
Robust workflow built for chemical genomic screening

Bioscience
Cell atlas offers clues to how childhood leukemia takes hold

Bioscience
Hidden flexibility in plant communication revealed

Bioscience
Harnessing the unintended epigenetic side effects of genome editing
Bioscience
Mica enables simpler, sharper, and deeper single-particle tracking

Bioengineering
Cancer’s hidden sugar code opens diagnostic opportunities
Bioscience
AI speeds up human embryo model research
Bioscience



