Material Science and Engineering
Keeping it random
A nano-scale memristor is shown to have superior stability for random number generation as an integral part of secure data transmission.
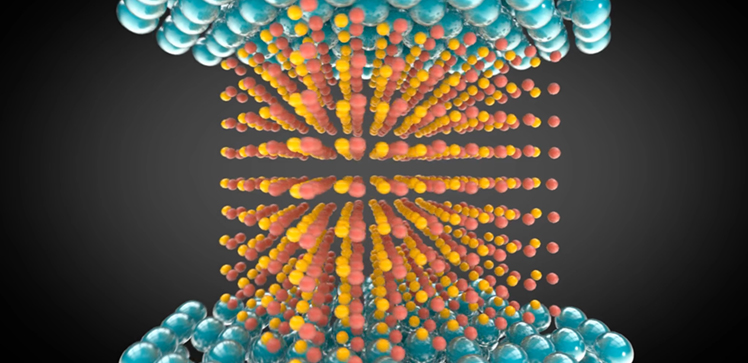
Using atomically thin two-dimensional films, KAUST researchers have developed a nano-scale random number generator with enhanced long-term stability and reduced power consumption. © 2021 KAUST; Anastasia Serin. /en/article/1168/keeping-it-random
Using atomically thin two-dimensional films, KAUST researchers have developed a nano-scale random number generator with enhanced long-term stability and reduced power consumption. © 2021 KAUST; Anastasia Serin. /en/article/1168/keeping-it-random
Using atomically thin two-dimensional films, researchers have developed a nano-scale random number generator with enhanced long-term stability and reduced power consumption.
Random number generation is a critical underlying function of secure data transmission, used to encrypt and secure data and generate one-time passwords. To generate a random number, a circuit detects the random noise produced by a physical component, such as the thermal noise from diodes or resistors. However, the power consumption of these elements can be significant in highly integrated low-power applications, and the degree of randomness can degrade over time due to a change in the device’s physical and electronic characteristics.
Mario Lanza, who joined KAUST in 2020, saw an opportunity for nano-scale devices called memristors to be used as more reliable true random number generators (TRNGs).
Memristors have fast operating speeds, low energy consumption and long endurance and data retention time, while being cheap and easy to fabricate.
© 2021 KAUST; Anastasia Serin.
“Memristors are meta/insulator/metal nanocells based on two-dimensional materials that have fast operation speed, low energy consumption and very long endurance and data retention time, as well as being very easy and cheap to fabricate,” says Lanza. “For this reason, memristors are being intensively explored for applications such as high-density electronic memories. They are also particularly useful for encryption systems because they can produce fluctuating electronic signals with an extraordinarily high degree of randomness.”
Memristors, short for “memory resistors,” are tiny passive electronic components that have a resistance that can be switched between two states by applying electrical stress. However, they also produce a type of electrical noise called random telegraphic noise (RTN), sometimes called popcorn noise for the sound it would make if connected to a speaker, which turns out to be perfect for random number generation. The challenge for Lanza’s team was to design and fabricate a memristor device that has stable RTN over time.

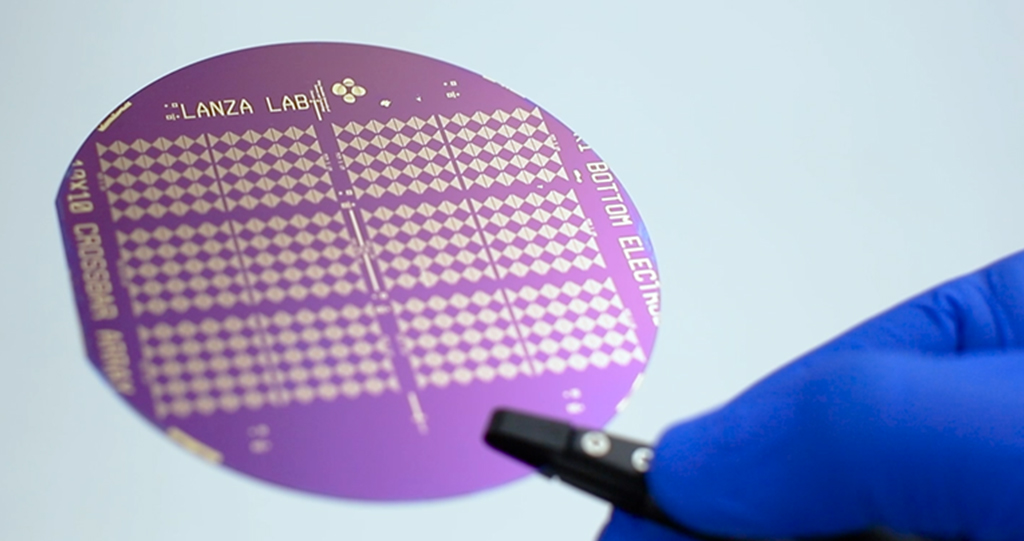
Mario Lanza (left) and his team fabricated hundreds of devices using industry-compatible methods to demonstrate scalability and compatibility with industry.
© 2021 KAUST; Anastasia Serin.
“The main challenge was that the atomic structure of the resistive thin film degrades over time, which causes the RTN signal to disappear,” says Lanza. “In our devices, we used two-dimensional multilayer hexagonal boron nitride, which is a two-dimensional material that has a very stable atomic structure and is immune to this effect.”
The team fabricated hundreds of devices using industry-compatible methods and characterized them using a range of techniques including a randomness test involving the generation of one-time passwords.

The team used two-dimensional multilayer hexagonal boron nitride, which is immune to the effects of degradation of the atomic structure of the resistive thin film.
© 2021 KAUST; Anastasia Serin.
“A key aspect of our work was the use of fabrication processes that are compatible with industry, which facilitates integration in commercial products,” Lanza says. “We also presented yield and variability information for hundreds of devices; it was a tremendous effort, but it gives more reliability to our study.”
References
- Wen, C., Li, X., Zanotti, T., Puglisi, F.M., Shi, Y., Saiz, F., Antidormi, A., Roche, S., Zheng, W., Liang, X., Hu, J., Duhm, S., Roldan, J.B., Wu, T., Chen, V., Pop, E., Garrido, B., Zhu, K., Hui, F. & Lanza, M. Advanced data encryption using 2D materials. Advanced Materials 33, 2100185 (2021).| article
You might also like

Chemistry
Turning infrared solar photons into hydrogen fuel
Applied Physics
A single additive enables long-life, high-voltage sodium batteries

Bioengineering
Smart patch detects allergies before symptoms strike
Applied Physics
Two-dimensional altermagnets could power waste heat recovery
Applied Physics
Interface engineering unlocks efficient, stable solar cells

Applied Physics
The right salt supercharges battery lifespan
Applied Physics
Light-powered ‘smart vision’ memories take a leap forward

Applied Physics




