Chemical Engineering
Fuel chemistry distilled
A new conceptual model for describing a fuel’s composition can accelerate and simplify combustion simulations.
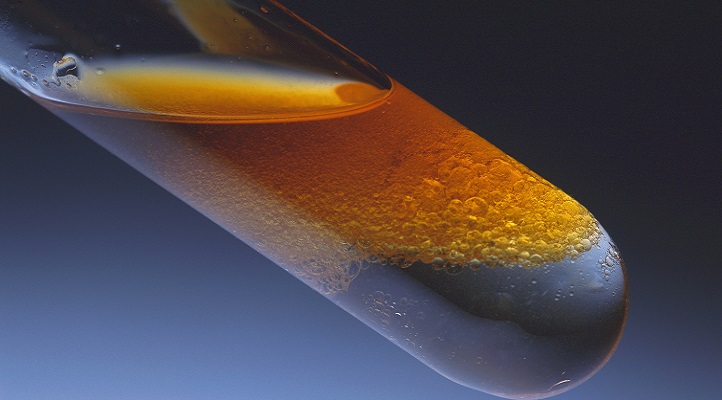

The gasoline and diesel we pump into our vehicles is a complex cocktail that can contain thousands of different chemicals. But look closer at the fuel, and the overwhelming complexity starts to resolve itself, KAUST researchers have shown.
Rather than try to model fuel combustion based on the long list of molecules the fuel contains, the researchers found a shorthand: they now show that they can distill the complexity into a very short list of molecular subunits or functional groups most fuel molecules are made from. This radically simplified method for accurately simulating fuel combustion was developed by Ph.D. student Abdul Gani Abdul Jameel with Mani Sarathy and team.
The project began with the hypothesis that the combustion behavior of each component of a fuel is dictated by the functional groups it comprises. To corroborate the theory, the team performed high-resolution nuclear magnetic resonance analysis in KAUST’s Core Labs to identify the main functional groups in a series of complex fuels. They then made simple surrogates for each fuel by selecting one or two molecules that contained the functional groups in the same balance as the real fuel.
Comparing key combustion parameters, such as ignition delay time and smoke point in the lab, the researchers confirmed the simple surrogates were faithful mimics of the real fuel. They showed a good surrogate needed to match the average molecular weight and contain the right proportions of just five key carbon-hydrogen functional groups: CH3, paraffinic CH2, paraffinic CH, naphthenic CH–CH2 and aromatic C–CH.
Traditional combustion modeling accurately captures the behavior of fuel mixtures by adding detailed chemical kinetics data for increasingly more of the components in the fuel, but the drawback is that the simulation becomes prohibitively slow to run. “We have shown that adding complexity to models is not necessary, as long as underlying features of simpler molecular parameters, the functional groups, are captured,” Sarathy says.
The team’s method for making simple fuel surrogates will directly improve the design of efficient new engines, explains Abdul Jameel. “Using a minimal number of components significantly reduces the time involved in developing chemical kinetic models and the computational expenses involved in simulating combustion in internal combustion engines,” he says.
But the team’s functional-group-based approach will reach far beyond surrogate formulation. “We are currently developing machine-learning-based models to predict the combustion properties of fuels based on their functional groups,” Abdul Jameel adds.
References
- Abdul Jameel, A. G., Nasera, N., Issayeva, G., Touitoub, J., Ghosh, M.K., Emwas, A-H., Farooq, A., Doley, S. & Sarathy, S. M. A minimalist functional group (MFG) approach for surrogate fuel formulation. Combustion and Flame 192, 250-271 (2018).| article
You might also like

Chemical Engineering
Urban air pollution goes up in smoke

Chemical Engineering
Rethinking machine learning for frontier science

Chemical Engineering
Magnetic nanoparticles capture microplastics from water

Chemical Engineering
Biogas upgrading goes with a swing

Chemical Engineering
Stronger, lighter, cheaper: a new route to carbon fiber production

Chemical Engineering
Unveiling the role of biomass-burning aerosols in atmospheric reactions

Chemical Engineering
Slashing industrial emissions using a hybrid model approach
Chemical Engineering




